
Threats from Malware and Ransomware are Rapidly Growing
With the increase in Malware and Ransomware attacks, reliability and data integrity are now at the forefront of business concerns and a primary challenge for businesses to solve. In this article, we review Ransomware detection and recovery architectures, including immutable backups and air-gapped systems.
We also review the HPE Shadowbase Ransomware architecture that assists businesses with thwarting this growing set of unique challenges and how the solution is evolving.
Note: This article is based on a presentation and demo given by Gravic at the Connect NonStop Technical Boot Camp in September 2023. Text from various slides is duplicated on the page to allow our international readers to use translation tools.
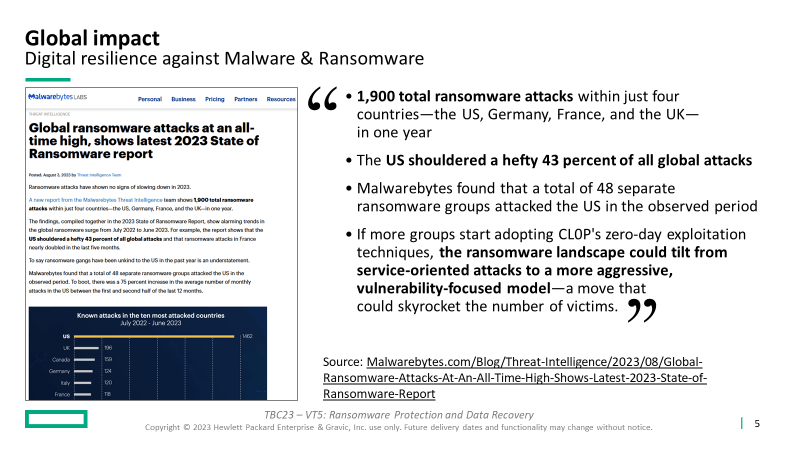
According to Malwarebytes (source: https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/threat-intelligence/2023/08/global-ransomware-attacks-at-an-all-time-high-shows-latest-2023-state-of-ransomware-report):
- “1,900 total ransomware attacks within just four countries—the US, Germany, France, and the UK – in one year”
- “The US shouldered a hefty 43 percent of all global attacks”
- “Malwarebytes found that a total of 48 separate ransomware groups attacked the US in the observed period”
- “If more groups start adopting CL0P’s zero-day exploitation techniques, the ransomware landscape could tilt from service-oriented attacks to a more aggressive, vulnerability-focused model—a move that could skyrocket the number of victims.”
Clearly, Ransomware is here to stay.
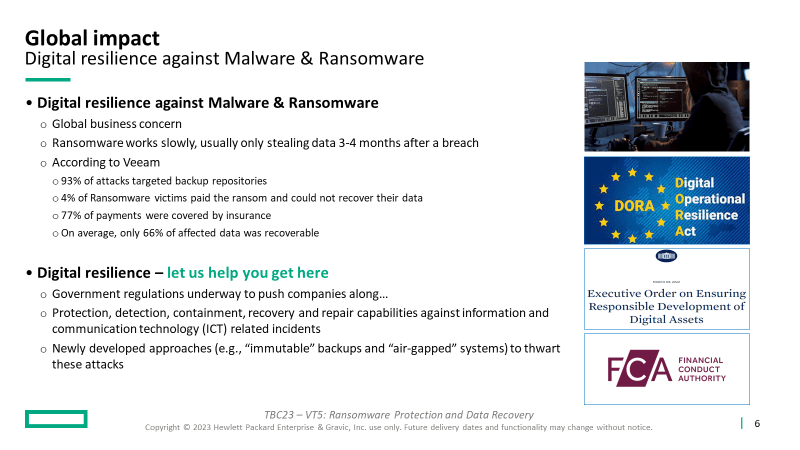
At the 2023 HPE Discover show, Veeam presented research from surveying thousands of their customers:
- “93% of attacks targeted backup repositories”
- “4% of Ransomware victims paid the ransom and could not recover their data”
- “77% of payments were covered by insurance”
- “On average, only 66% of affected data was recoverable”
Malware and Ransomware have a global impact for businesses of all kinds and are spurring regulatory mandates across the globe.
- Digital resilience
- According to the European Union’s DORA Act, digital resilience is the “protection, detection, containment, recovery and repair capabilities against information and communication technology (ICT) related incidents”
- U. S. Executive Orders have been released to address digital resilience from an infrastructure and hardware perspective, with many more regulations to come as DORA and the digital resilience landscape evolves
- Ransomware
- New approaches are available to combat these challenges such as “immutable backups” and “air-gapped” systems
- HPE NonStop provides a layer of protection with TMF-audited applications
- Data replication using audited environments will not spread ransomware
- Virtualization
- Virtual environments such as AWS S3 can provide immutable (unchangeable) offsite storage to store critical enterprise data
- HPE Shadowbase software provides high availability for virtual environments just like it always has for physical ones
- GreenLake
-
- HPE Shadowbase software fits seamlessly into GreenLake environments
- HPE provides Managed Services which satisfies the “people-gapping” requirement of a Ransomware and Malware recovery solution
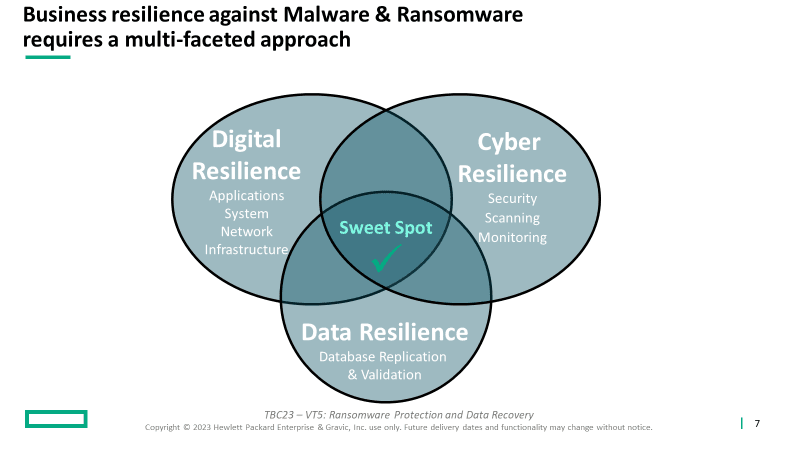
Business resilience solutions that can successfully defend against Malware and Ransomware require a multi-faceted approach. For these three key pieces, these are their main areas of focus:
-
- Digital Resilience – redundant and resilient Infrastructure
- Cyber Resilience – monitoring system activity and traffic and securing the environment from unauthorized access
- Data Resilience – database replication and validation
-
- Always remember the 3-2-1-1 rule:
- 3 data copies
- 2 different storage media
- at least 1 copy off-site
- at least 1 in immutable storage (managed by different staff)
- Always remember the 3-2-1-1 rule:
-

Background
Many HPE NonStop customers are easily overwhelmed when strategizing Malware and Ransomware recovery solutions. A great place to start is by defining the problem:
1. Know your enemy – Malware and Ransomware are similar, but different:
-
-
- Malware – software that is specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system (dictionary.com)
- Ransomware – malicious software designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money is paid (dictionary.com)
-
2. Resilience against each is (a bit) different – multiple products are required to create an overarching solution and must be coordinated.
3. Detection and recovery is not the same thing as prevention
-
-
- Today, state-of-the-art is post-event detection and recovery
- The future needs to focus on identifying the attack early and preventing it from having an impact
-
4. HPE Shadowbase software currently provides data resilience for detection and recovery.
5. However, HPE Shadowbase software is only one piece of the solution – for example, malware that stealthily steals data requires additional counter-measures.
6. The Gravic Validation Architecture (VA) is a new technology being developed to immediately detect and prevent data corruption.
On HPE NonStop, TMF is your first line of defense!
Non-audited data does not have the same advantages, capabilities, nor protection.
In a non-audited environment, if malware invaded and performed data tampering – how would you know?
Using TMF guarantees all database changes are logged and therefore, can be leveraged for recovery. Simply put, this leverage is not always possible in a non-audited environment.
HPE Shadowbase Digital Resilience Provides Unique Capabilities
HPE Shadowbase software integrates with TMF to extract database change data, fingerprints messages to detect interprocess message tampering, and fingerprints its intermediate Queue Files to detect data tampering.
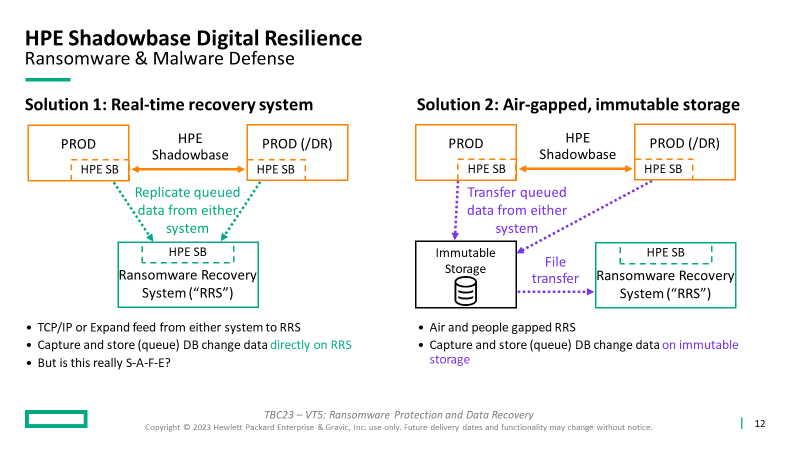
Two (currently available) solutions that provide Ransomware and Malware Defense Include
-
-
- Real-time recovery system
- Capture database change data into Shadowbase Queue Files
- Queued data is replicated from either system (production or DR) to the Ransomware Recovery System (RRS)
- Data can be fed via TCP/IP or Expand from either system to the RRS
- Allows capturing and storing (queuing) of the database change data directly on the RRS, readily available for replay
- But is this really S-A-F-E? It certainly is not air-gapped; an attack that propagates via Expand or TCP/IP may infect the RRS; hence, this is not a preferred solution nor a best practice
- Air-gapped, immutable storage
- Capture database change data into Shadowbase Queue Files
- Transfer the captured/queued data from either system to immutable storage
- Periodically transfer the captured/queued data from immutable storage to the RRS
- This transfer allows the RRS to be air-gapped and people-gapped, both of which are important to protect against malware and ransomware infection
- Real-time recovery system
-
Both options:
- The customer decides how often to synchronize the RRS database to bring it current
- After an attack, recover the application and operations on the RRS to continue production processing, which supports subsequent forensics and root cause analysis on the compromised system
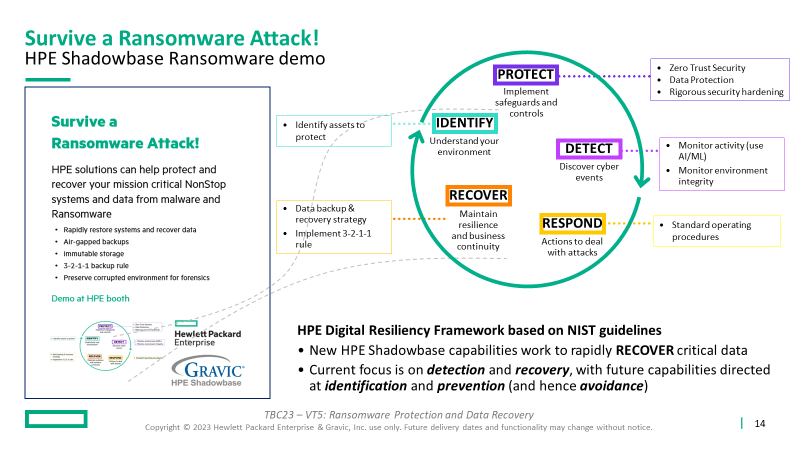
How to Survive a Ransomware Attack
This solution features key products available from the HPE product suite, including HPE Shadowbase Ransomware, to build out a malware and ransomware defense architecture to allow your business to survive, successfully recover from an attack, and preserve the original infected environment for subsequent analysis and forensics.
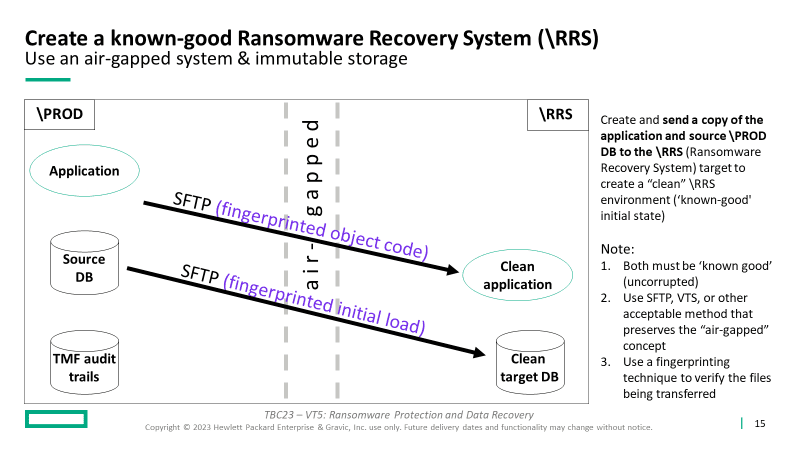
Initially, and periodically, create and send a copy of the application and source \PROD DB to the \RRS (Ransomware Recovery System) target to create a “clean” \RRS environment (‘known good’ initial state).
Note:
- Both must be ‘known good’ (uncorrupted)
- Use SFTP, VTS, or another acceptable method that preserves the “air-gapped” concept (including tapes and “sneaker net” if you prefer)
- Use a fingerprinting technique to verify the files being transferred
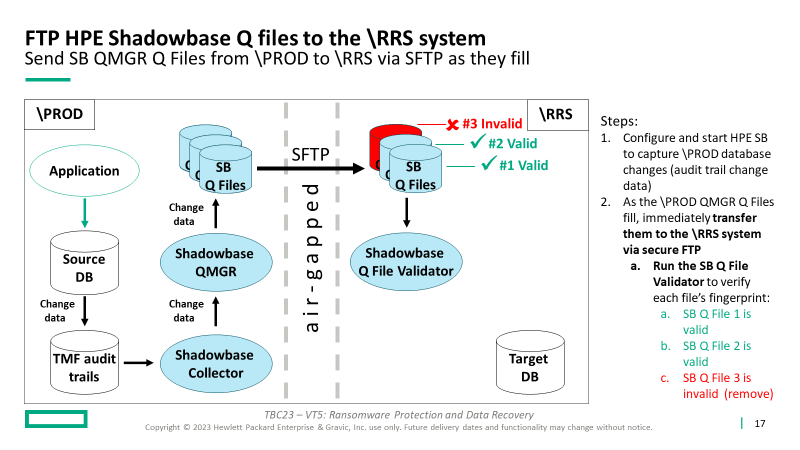
Steps:
1. Configure and start HPE SB to capture production (\PROD) database changes (audit trail change data)
2. As the \PROD QMGR Queue Files fill, immediately transfer them to the \RRS system via secure FTP (or into immutable storage, then to the \RRS)
-
-
-
- Run the SB Queue File Validator to verify each Queue File’s fingerprint (in this example, Queue File #3 has been corrupted):
-
- SB Q File 1 is valid
- SB Q File 2 is valid
- SB Q File 3 is invalid (remove)
- This step triggers the recovery process
-
- Run the SB Queue File Validator to verify each Queue File’s fingerprint (in this example, Queue File #3 has been corrupted):
-
-
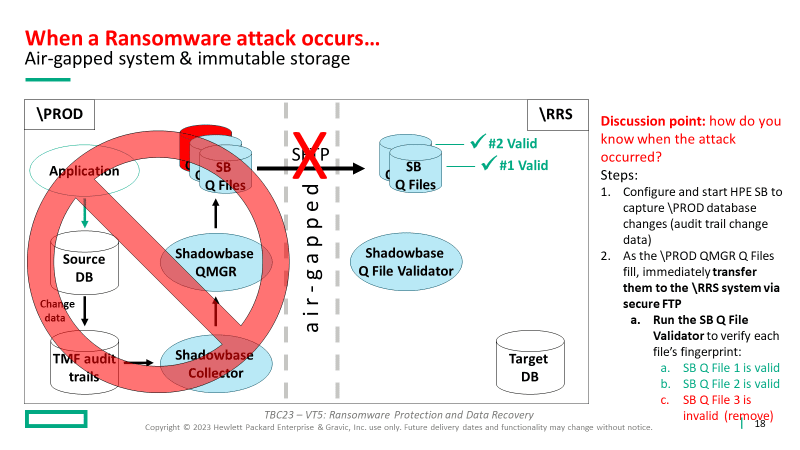
Once the invalid Q File is discovered and removed, the recovery sequence occurs:
3. Start Shadowbase replication and replay the valid Queue Files (SB Queue Files 1 and 2) to bring the \RRS database current (at least to the point where production corruption occurred)
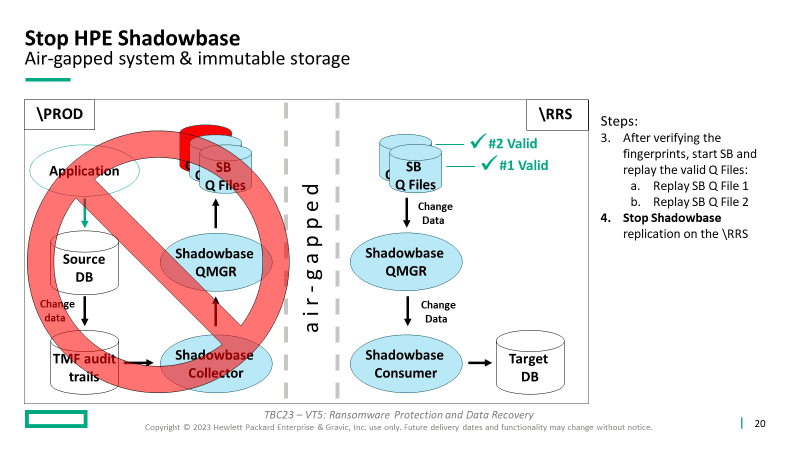
- Stop Shadowbase replication on the \RRS
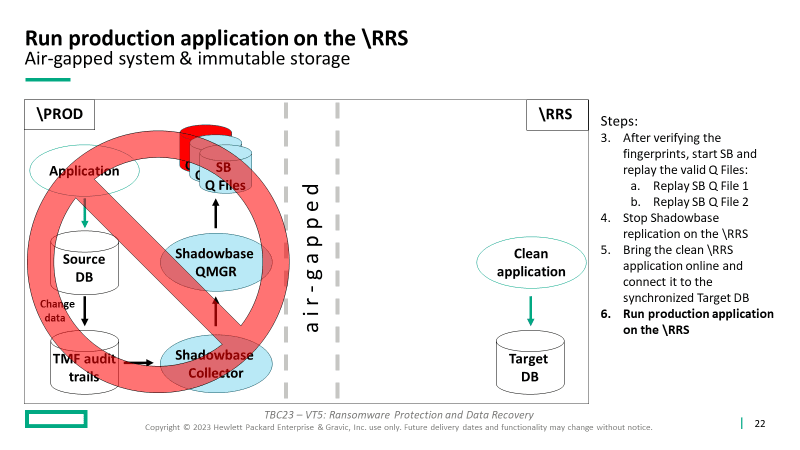
5. Bring the “known clean” (known good) RRS application online
6. Connect the users to the RRS
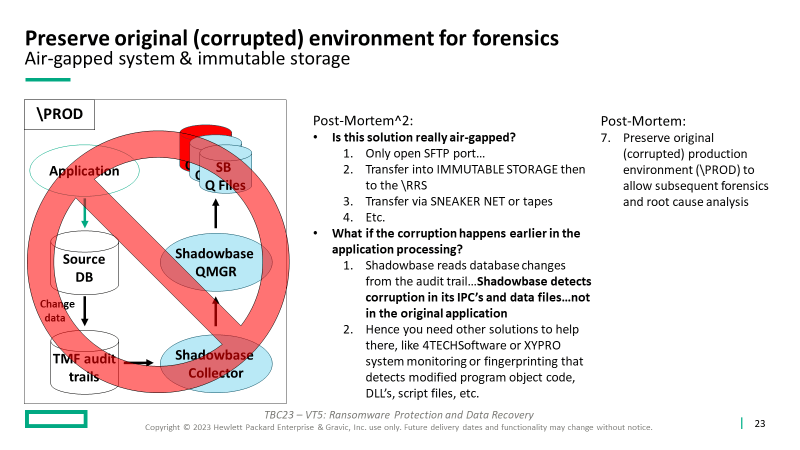
7. Preserve original (corrupted) production environment (\PROD) to allow subsequent forensics and root cause analysis (to catch the perpetrators)
Summary:
-
- Digital resilience solutions require a multi-faceted approach
- Create a Ransomware Recovery Solution (RRS) system using HPE Shadowbase Ransomware
- Protect your data using Shadowbase fingerprinting
- Respond to attacks using automated recovery procedures
- Recover critical data along with application services
- Be on the lookout for future developments of Gravic’s Validation Architectures (VA) to learn how Gravic’s VA can help identify and prevent attacks (which is much easier than having to detect and recover)
Thanks for Reading!
Technology is often the limiting factor. With the right people and the right solutions like HPE Shadowbase software; that’s where the magic happens!
HPE Shadowbase software is HPE’s strategic go-forward data replication and streaming solution, globally sold and supported by HPE or HPE’s regional reseller. Contact your HPE representative or Gravic at www.ShadowbaseSoftware.com for more information.


Be the first to comment